Every successful business owner aims to expand production capacity, increase output, and enter new markets. However, scaling a manufacturing business comes with significant risks. But what if a company could process more orders without wasting additional time and money?
This article opens a series dedicated to ERP solutions for manufacturers. We explore why production scaling often fails, what challenges business owners face along the way, how those challenges can be addressed, and why ERP plays a critical role in sustainable growth.
Manufacturing Trends and the Global Market Landscape
After the global pandemic of 2020, businesses entered a new operating reality shaped by geopolitical uncertainty, energy challenges, and rapid technological advancement.
For manufacturing companies worldwide, scaling is no longer just about producing more. Growth now requires digital readiness, operational resilience, efficient resource management, and the ability to adapt quickly to change. To understand today’s dynamics, let’s look at key industry trends.
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), global manufacturing output grew by 1.3% in Q1 2025 compared to Q4 2024. The primary growth drivers include artificial intelligence adoption and increased defense-related investments.
- Modern manufacturing growth follows three core directions: technology, operational efficiency, and financial management. High-performing companies align all three within a single, coherent strategy.
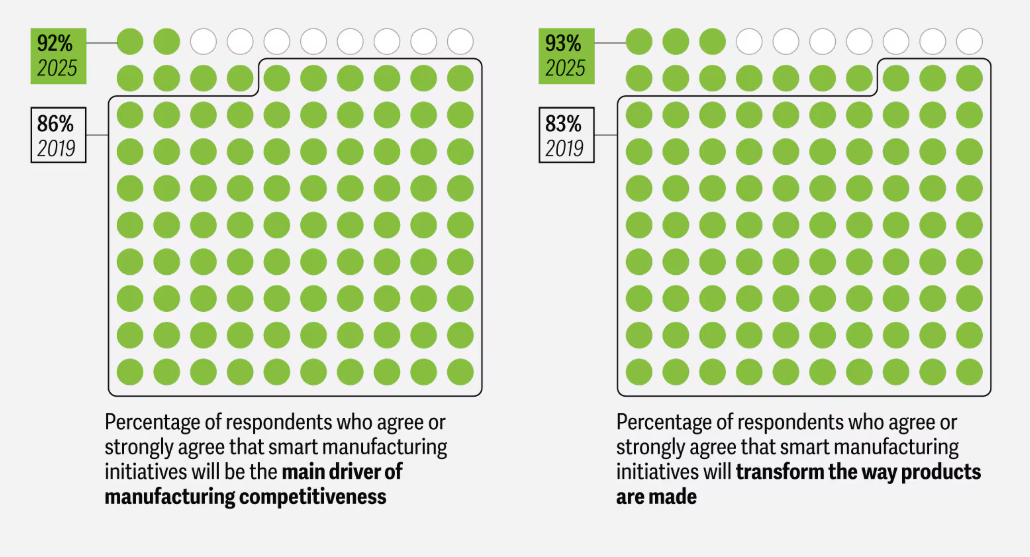
- A Deloitte survey found that 92% of manufacturers consider “smart manufacturing” the most important factor for competitiveness over the next three years. This concept goes beyond automating individual production lines, it involves building an integrated ecosystem where data drives every stage of the manufacturing process.
- Leading manufacturers are actively investing in cloud technologies (57%), Industrial IoT (46%), and AI and machine learning (29%). At the same time, scaling increasingly depends on workforce enablement and the ability to work effectively with new digital tools.
Production capacity utilization has also increased across multiple industries, including pharmaceuticals, furniture and woodworking, food production, and textiles.
Key Challenges Facing the Manufacturing Sector
Despite rapid technological progress, manufacturers continue to face structural and operational barriers:
- Energy and infrastructure constraints. Limited or unstable energy infrastructure increases operational costs and restricts the development of high-tech production environments.
- Trade and regulatory uncertainty. Fluctuating tariffs and changing trade policies force manufacturers to hold excess inventory, diversify suppliers, or pass additional costs on to customers.
- Labor shortages and rising costs. A global shortage of skilled workers – particularly in technical and engineering roles – drives up labor costs and limits productivity.
Additional global challenges include volatile raw material prices, supply chain disruptions, access to capital, and growing cybersecurity risks.
What Prevents Effective Strategic Scaling?
According to Strategy Ladders, more than 70% of strategic growth initiatives fail to achieve their objectives. The reasons are rarely external alone – most failures stem from internal limitations.
Low Operational Maturity
Ambitious growth strategies often ignore the physical and operational limits of production systems. Expanding sales or marketing without aligning manufacturing capacity leads to missed deadlines, quality issues, and reputational damage.
How to address it? Modernize core systems and review growth strategies regularly – monthly or quarterly – to ensure alignment with real operational capabilities.
Process Inertia
Success in a niche market does not guarantee scalable success. Launching large production volumes without validating demand results in excess costs and underutilized resources. Overreliance on a single partner or sales channel further increases business risk.
Management and Organizational Culture
Many companies struggle to scale because decision-making remains centralized. When all approvals depend on founders or top executives, organizations lose agility.
Rapid headcount growth without structured onboarding creates confusion and lowers performance. Resistance to change also plays a major role – studies show that up to 68% of digital transformation initiatives fail due to employee resistance or lack of understanding.
Lack of Process Transparency
When departments operate in silos, no one has a complete view of the business. Engineering, procurement, production, and management teams work with fragmented data, leading to misalignment, last-minute decisions, and inefficiencies.
As a result, teams spend excessive time searching for information instead of executing production tasks.
Excessive Manual Work and Poor Integration
Spreadsheets, legacy systems, and disconnected tools may work at an early stage but become a serious bottleneck during growth. Re-entering the same data across multiple systems is a clear sign that the business is not ready to scale.

Strategies for Sustainable Manufacturing Growth
Sustainable scaling requires a deliberate, data-driven approach. The following strategies help manufacturers build resilience and prepare for long-term growth:
- Operational resilience first. Investments in energy independence and diversified supply chains are critical for business continuity.
- Gradual digitalization. Instead of attempting a full-scale transformation at once, focus on operational bottlenecks where automation and AI can deliver quick wins.
- Capital flexibility. Maintaining liquidity and optimizing cash flow is essential during periods of economic volatility.
- People-centric growth. Scaling is impossible without investing in employee training, leadership development, and corporate culture.
In today’s manufacturing environment, adaptability matters more than asset size. In 2026 and beyond, successful companies will scale through “smart growth” powered by data, efficiency, and human potential.
How ERP Improves Operational Efficiency and Enables Growth?
A well-implemented ERP system is the foundation of predictable and controlled manufacturing scale.
ERP enables companies to manage daily operations while planning growth with greater speed, visibility, and accuracy. For business owners focused on profitable expansion, ERP fundamentally changes how decisions are made.
By centralizing data across departments, ERP ensures transparency, control, and consistency. Unified information supports standardized processes, accurate cost tracking, and informed decision-making across production, supply chain, sales, and finance.
Automation allows manufacturers to increase output without proportional headcount growth. Real-time dashboards provide full visibility into production status, deadlines, delays, and bottlenecks.
Odoo Manufacturing integrates resource planning (MRP), inventory and warehouse management, quality control, cost and performance tracking, analytics, and reporting. These modules work seamlessly with sales, procurement, and finance, delivering process transparency, efficient resource utilization, and predictable production outcomes.
(Learn more in our dedicated article: Odoo for Manufacturing — Automation, Control, and Process Transparency.)
Conclusion
Successful manufacturing scaling is built on the intersection of data, technology, and people. Companies that recognize this and act decisively will secure long-term competitive advantage.
Sustainable growth depends on strategic preparation, operational maturity, and the ability to adapt continuously. Manufacturers that align these elements today are shaping the future of the industry.
FAQ
Manufacturing scaling is the process of increasing production capacity to meet higher demand while maintaining cost control, quality, and efficiency.
Manufacturing scaling fails because of manual processes, poor planning, lack of data visibility, and disconnected systems that cannot support growth.
ERP helps scale manufacturing by automating processes, centralizing data, and improving planning across production, inventory, and finance.
A manufacturing company should use ERP when spreadsheets and manual work slow down operations and limit production growth.
ERP improves efficiency, reduces errors, increases visibility, and supports sustainable manufacturing growth.
