The US ERP market is evolving rapidly, driven by cloud adoption and AI integration. Companies are investing in ERP not just to streamline operations, but to unlock strategic value and stay competitive. In this report, we have analyzed market data and insights to provide a comprehensive overview of trends, adoption patterns, and growth projections through 2032.
US Automation Market Overview: ERP Takes Center Stage
The global industrial automation market continues to grow steadily, with projections reaching $322.7 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 8.2%. This growth highlights that companies worldwide are actively investing in digitalizing manufacturing processes to improve efficiency, automate routine tasks, and reduce operational costs.
At the same time, the enterprise software segment — particularly ERP systems — is outpacing broader automation growth. In 2022, the global ERP market was valued at $53.8 billion, and it is expected to reach $123.4 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 11.1%. This underscores the increasing strategic priority for organizations, especially in the US, to modernize their internal operations and leverage integrated business platforms.

This trend indicates that businesses are prioritizing not just manufacturing automation, but also the modernization of internal operational systems — including finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer engagement.
In the United States alone, ERP spending is projected to reach $62.6 billion, accounting for nearly 43% of the global ERP market. This underscores the strategic importance of the US market for ERP vendors and reflects the high level of digital maturity and investment capacity among American enterprises.
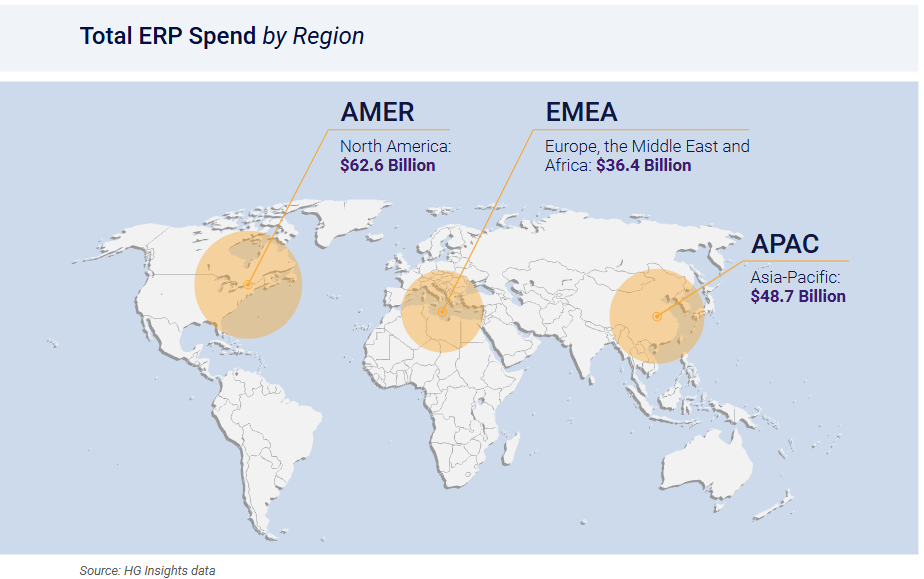
This concentration of investment reflects:
- the high level of digital maturity among American companies,
- the strong investment capacity of US businesses, and
- the strategic importance of the United States for global ERP vendors.
According to HG Insights, there are seven primary ERP application areas, with companies allocating the largest shares of spending to financial modules (27%) and human capital management (23%), as these functions are the most frequently targeted for automation.

So today, ERP in the United States is no longer just an accounting or automation tool. It has become a strategic platform for business transformation. Modern ERP integrates artificial intelligence, cloud solutions, and real-time analytics, serving as the core of a company’s digital ecosystem. Through ERP, data flows seamlessly, enabling analytics, automation, and innovation. This central role explains why ERP investments are growing even faster than the broader industrial automation market.
ERP Implementation by Business Size
Research shows that ERP adoption continues to rise across industries, driven by the need for comprehensive solutions capable of managing complex business processes. As companies seek to optimize operations, demand grows for integrated ERP platforms that provide robust supply chain management and industry-specific functionalities.
Large Enterprises (LE)
For large corporations, ERP systems have long been the foundation of strategic transformation. They support revenue generation, market expansion, and product innovation. These organizations are increasingly integrating AI into their ERP solutions. By 2026, it is expected that 40% of Global 2000 companies will leverage Generative AI to create customized business solutions.
Medium Businesses (MB)
Medium-sized companies are actively adopting cloud ERP systems to improve interdepartmental collaboration and enhance transparency across corporate processes. During periods of growth—often accompanied by market uncertainty—these businesses need a single, integrated system that consolidates financial data and customer information, enabling more effective decision-making and business management.
Small Businesses (SB) and SMEs
ERP is now critical even for small and medium-sized enterprises. Over 80% of SMEs with annual revenues under $50 million rely on ERP to boost operational efficiency and gain better control over processes. Key outcomes of ERP adoption in this segment include:
- Inventory optimization: 91% of companies
- Cost reduction in procurement and inventory management: 62%
- Increased productivity: 78%
When selecting an ERP system, the majority of companies (89%) focus on core financial functions, such as accounting.
Small and medium businesses benefit quickly from ERP because their goals are specific and concrete, while large enterprises use ERP as a strategic transformation tool, integrating AI to achieve long-term, complex business objectives.
We recommend to read article The Future of ERP: 9 Innovations Businesses Can’t Afford to Miss in 2026
ERP Users by Industry
Companies that have relied on core ERP systems for over 10 years are distributed across several industries. The breakdown of long-term ERP users by sector is as follows:
- Manufacturing
- Finance and Insurance
- Public Administration
Top ERP-Spending Industries
Industries that spend the most on ERP systems clearly prioritize automation and digital transformation. Leaders in this ranking actively invest in integrated platforms to manage finance, manufacturing, supply chains, and other critical business processes, aiming to boost operational efficiency and maintain a competitive edge.

Key ERP Technology Trends
The US ERP market is evolving rapidly, moving from simple process automation to intelligent business transformation. Here’s a brief overview of the main technology trends shaping ERP in the coming years:
AI Moves from Optional to Essential
Artificial intelligence is now a critical component of ERP systems. Companies are integrating AI/ML not just to analyze data, but to predict issues and support real-time decision-making, making AI a core driver of business success.
Generative AI + ERP = Next-Level Efficiency
Generative AI is redefining automation. Combined with cloud ERP, it enables businesses to reengineer processes, improve transparency and agility, and deliver immediate value to employees and customers. Beyond optimization, it serves as a platform for new business models and innovation.
RPA and Industry-Specific Solutions Remain Relevant
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) continues to thrive, especially in manufacturing, technology, and healthcare. Demand for industry-specific ERP solutions is increasing as companies seek systems tailored to their unique operational needs.
The Main Trend: From Automation to Augmentation
The market is shifting from automating tasks to augmenting human capabilities. ERP systems now help employees work more strategically, not just more efficiently. Companies that successfully integrate Generative AI deeply into their operations will gain a significant competitive advantage.
For a detailed look at all ERP innovations, see our full article - Top ERP Trends for 2026.
ERP Growth Barriers: Main Challenges Explained
Despite active technology adoption, large-scale automation in US companies faces three interconnected challenges. Without addressing them, investments in ERP and AI may fail to deliver expected value.
Organizational Readiness and Cultural Resistance
The Challenge: Many companies adopt technology faster than they can effectively utilize it. This has led to a growing share of “underachievers”—organizations that invest in AI/ERP but fail to realize expected benefits.
Key Causes:
- Lack of executive support
- Insufficient post-launch system maintenance and guidance
Strategic Response: Companies must build internal buy-in for change. Employees should see tangible benefits from new tools—like Generative AI—that make their work immediately more productive. This helps foster a culture ready for broader digital transformation.
Technology Talent Shortage
The Challenge: Talent gaps are a critical operational barrier. There are two key areas of shortage:
- Legacy system experts (SAP, Oracle, etc.)
- Modern technology specialists (Cloud, AI, ML)
- 37% of companies delay or cancel projects
- 42% slow down modernization initiatives
- 36% experience productivity losses
Strategic Response — Companies need a balanced approach:
- Maintain expertise in legacy systems while integrating new technologies
- Invest in retaining experienced staff and actively hiring Cloud/AI talent
Top Hiring Priorities: Cybersecurity, multi-cloud expertise, ERP integrations
AI-Related Risks
The Challenge: As AI becomes more embedded in ERP — especially in finance and logistics — poor risk management (biased algorithms, regulatory non-compliance, lack of transparency) can threaten the entire organization.
Strategic Response: Implement clear AI governance frameworks that cover ethical standards, transparency, and regulatory compliance. High-performing "transformer" companies focus on four actions:
- Building a supportive culture.
- Redesigning operational processes.
- Aligning AI deployment with organizational maturity.
- Starting with proven use cases.
Systemic Interdependence of Barriers
These challenges do not exist in isolation—they are deeply interconnected. For example:
Talent shortages → lack of post-launch support → poor results → decreased executive confidence → weak AI risk management
Integrated Strategy for Success: To overcome barriers, companies must simultaneously address:
- Support for legacy systems and adoption of new technologies.
- Recruitment and retention of skilled IT professionals.
- Internal buy-in and cultural readiness.
- Enterprise-wide AI risk management.
Failing to tackle these areas in a coordinated way means even significant ERP and AI investments may fall short of delivering expected ROI.
Strategic ERP Market Outlook
The US ERP and business automation market is experiencing robust and accelerating growth that is expected to continue through 2032. Investments in Cloud ERP integrated with AI and Generative AI (GenAI) remain the most profitable and strategically critical, enabling companies not only to optimize operations but also to create new revenue streams and competitive advantages.
Key trends shaping the market forecast:
- Cloud ERP is set to become the leading market segment, reaching $176.9 billion by 2032, while the overall ERP market is projected to grow to $123.4 billion by 2030. The gap between on-premise and cloud solutions will widen. Companies delaying cloud adoption will face high maintenance costs and technological lag.
- Hyperautomation and intelligent augmentation. The nature of automation is evolving. Businesses will increasingly automate not only routine tasks but also complex cognitive functions, leveraging real-time analytics and predictive algorithms.
- Integrated approach for strategic success. Market leaders will combine technological speed, organizational agility, and robust risk management to achieve sustainable advantages.
By 2032, the market will be led by companies that embed Cloud ERP and AI/GenAI into their core business strategy, enabling rapid scaling of value and fostering an innovation-driven culture. Organizations that focus solely on technology without aligning organizational readiness risk falling behind and losing critical competitive edge.

